What Are The Challenges & Opportunities For Merchant Acquirers?
If you’ve ever wondered how your favorite local café accepts your credit card or how online stores process your payments so seamlessly, you’ve just scratched the surface of merchant acquiring.
This vital yet often overlooked part of the payment ecosystem is what makes it possible for businesses to accept card payments and boost their sales.
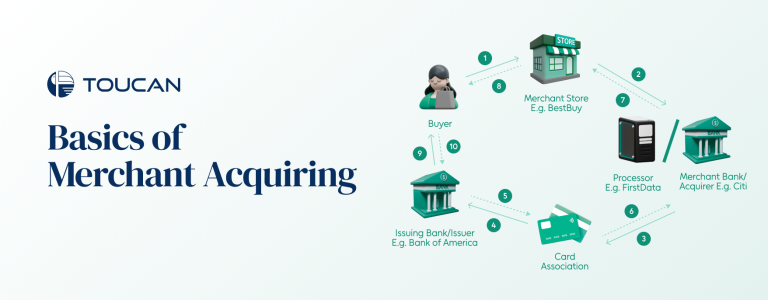
Merchant acquiring is the process that enables businesses (or merchants) to accept card payments from customers. Whether it’s a credit card, debit card, or even digital wallets linked to these cards, merchant acquiring ensures the payment gets processed securely and efficiently.
Here’s how it works:
The Customer Side: The transaction begins when a customer uses their card to make a payment. This card is linked to their issuing bank, which authorizes and verifies the payment.
The Merchant Side: The acquiring bank (or merchant acquirer) processes the transaction on behalf of the business. They handle everything from authorizing the payment to transferring the funds into the merchant’s account.
In essence, the merchant acquirer acts as the bridge connecting businesses with payment networks like Visa, Mastercard, or American Express.
Global Merchant Acquiring Industry: A Comprehensive Overview For Merchant Acquirers
The merchant acquiring industry is vast and varied, shaped by regional dynamics, technological advancements, and evolving customer preferences.
A Snapshot of the Global Merchant Acquiring Market
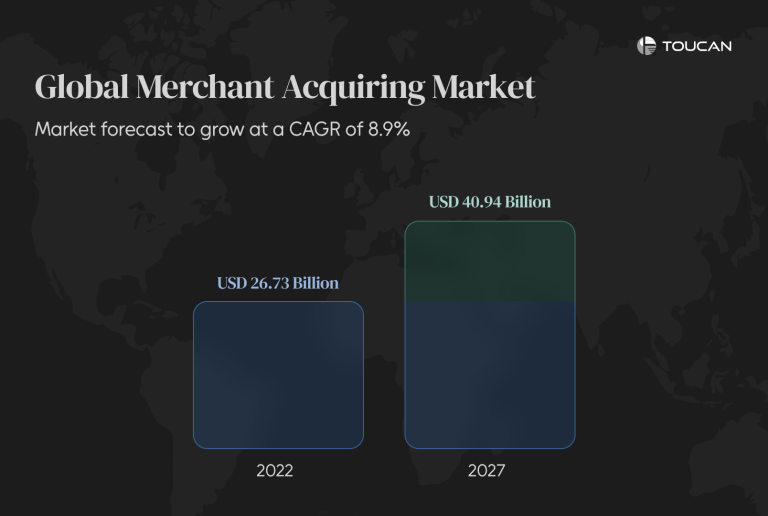
The global merchant acquiring market was valued at approximately $26.73 trillion in 2022, and it’s projected to reach nearly $40.94 trillion by 2027. This phenomenal growth is fueled by the rising adoption of digital payments, eCommerce expansion, and the push for financial inclusion in emerging markets.
Some key statistics include:
Top Acquirers: Dominated by major players like JPMorgan Chase, Worldpay, and Adyen, the market is heavily consolidated through mergers and revenue-sharing alliances.
Regional Dynamics: North America and Europe lead in market maturity, while Asia-Pacific and Latin America are experiencing rapid growth.
Market Drivers: Contactless payments, mobile wallets, and government initiatives promoting cashless economies.
Why Global Acquiring Matters
For businesses operating in multiple regions, global merchant acquiring offers a unified solution to streamline international transactions. Here’s why it’s essential:
Higher Transaction Success Rates: Acquirers optimize payment routing to minimize failed transactions, especially in cross-border scenarios.
Localized Payment Methods: Supporting popular local options like Alipay in China or UPI in India boosts customer satisfaction.
Regulatory Compliance: Acquirers handle complex compliance requirements across multiple jurisdictions, reducing business risks.
Currency Conversion: Seamless currency conversions enhance the customer experience and reduce friction in international sales.
Key Trends Shaping the Merchant Acquiring Landscape
The world of merchant acquiring is evolving at lightning speed, driven by regulatory changes, technological advancements, and shifting customer expectations.
For businesses, staying ahead means keeping a close eye on the trends reshaping this critical industry. Whether you’re a merchant, acquirer, or payment professional, understanding these developments can make all the difference.
3.1. Heightened Regulatory Scrutiny on Debit Interchange Fees
Governments worldwide are ramping up their focus on interchange fees, and for good reason. These fees, a percentage of every card transaction, have long been a point of contention between merchants and card networks.
Take the Durbin Amendment in the U.S., for example. It capped debit card interchange fees for regulated banks, benefiting small merchants by reducing costs. Similarly, the European Union’s Regulation 2015/751 set limits on interchange fees, encouraging broader card payment adoption.
For acquirers, this heightened scrutiny means balancing compliance with profitability.
3.2. The Independent Sales Agent vs. In-House Sales Force Dilemma
When it comes to expanding their reach, acquirers face a pivotal choice: rely on independent sales agents or build an in-house sales force. Each approach has its pros and cons.
Independent Sales Agents:
These agents bring flexibility and market expertise, but they often operate on commission, which can lead to inconsistencies in branding and customer experience.
In-House Sales Force:
An in-house team offers better control and alignment with company goals but comes with higher fixed costs for salaries, training, and infrastructure.
To succeed, acquirers are adopting hybrid models—leveraging the strengths of both approaches.
3.3. PCI-DSS Compliance: A Challenge for Small Merchants
The PCI-DSS is crucial for safeguarding cardholder data. However, small merchants often struggle to meet these stringent requirements.
Why is compliance so challenging?
Limited resources for implementing robust security measures.
A lack of awareness about PCI-DSS obligations.
High costs of securing payment infrastructure
3.4. The Crucial Need for Sales Agent Training and Education
As the merchant acquiring industry becomes more complex, well-informed sales agents are more critical than ever. Yet, many acquirers overlook the importance of continuous training and education for their sales teams.
Key areas of focus include:
Understanding Regulations: Sales agents need to be fluent in the latest regulatory changes, such as PCI-DSS updates and interchange fee caps.
Tech-Savviness: With new payment technologies emerging, agents must be able to explain and sell cutting-edge solutions to merchants.
Areas Of Focus For Merchant Acquirers
The merchant acquiring industry is evolving rapidly, with growing challenges stemming from the commoditization of services. Intense price competition is squeezing margins and driving consolidation across the sector. To remain competitive and thrive, merchant acquirers need to rethink their strategies. Let’s explore three key areas where merchant acquirers can focus their efforts to tackle these challenges head-on and fuel sustainable growth.
4.1. Innovative Pricing Strategies for Merchant Acquiring
Pricing strategies play a pivotal role in maintaining competitiveness. Acquirers generally employ one of three pricing models: interchange-plus, bundled pricing, or tiered pricing.
- Merchant Preferences: Most merchants prefer bundled and tiered pricing because they are straightforward, while interchange-plus, despite its transparency, involves complex calculations that many merchants avoid.
- Customizing Merchant Charges: Charges often vary by market due to differences in reporting, troubleshooting, and chargeback fees. In bundled and tiered pricing, all transaction types—credit, debit, card-present, and card-not-present—are priced uniformly, offering simplicity for merchants.
4.2. Strategic Technological Investments for Merchant Acquirers
Investing in the latest technology is crucial for acquirers to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and meet evolving market demands. However, many acquirers still operate on fragmented legacy systems that are inflexible and costly to maintain.
Key Focus Areas for Technology:
- Flexible Systems: Transitioning to flexible systems capable of supporting multi-country, multi-language, multi-currency, and multi-time zone operations can significantly enhance scalability and efficiency
- Legacy System Overhaul: Upgrading or replacing outdated mainframe systems in one go, rather than piecemeal, allows acquirers to better adapt to global requirements.
With the rapid growth of e-commerce, multichannel acquiring has become a key opportunity for acquirers to expand their service offerings.
Why Multichannel Acquiring Matters:
- Blurred Lines Between Channels: Modern commerce integrates online and offline sales, requiring acquirers to extend their capabilities beyond traditional payment acceptance.
- Room for Growth: Traditional acquirers have underinvested in online acquiring, leaving significant untapped potential in this space